EU Stock EnjoyCool Link is On Sale with $400 off!

How To Charge My LiFePO4 Batteries?
Over the past few years, lithium iron phosphate batteries(LFP) have become increasingly popular due to their safety, long lifespan and fast charging capabilities. If you’re an owner of LFP batteries, it’s important to understand the proper charging methods to maximize your batteries’ performance and longevity. In this article, we will discuss the common charging techniques, whether lead-acid chargers can be used, important precautions and matters regarding long-term storage.
Common charging methods
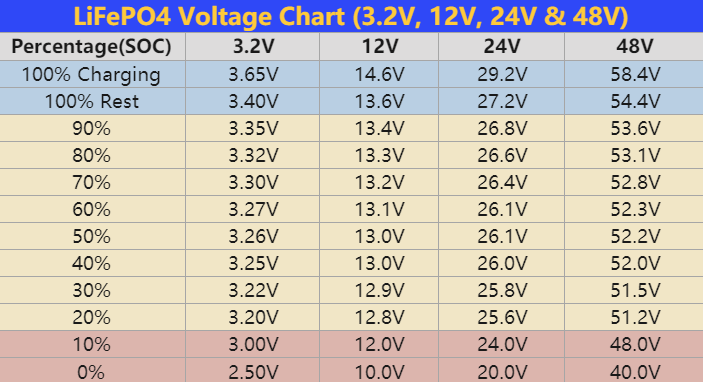
The most effective way to charge LFP batteries is with a lithium iron phosphate battery charger. LFP batteries have a nominal voltage of 3.2V per cell and require charging voltages between 3.6V to 3.65V maximum.
Most LFP chargers follow a simple two-stage process:
Constant Current Charging (CCC): The charger outputs a constant current, usually 0.3C to 1C of the battery’s rated capacity. This brings the battery to around 90-95% state of charge.
Constant Voltage Charging (CVC): The charger then switches to a constant voltage charge stage, typically set at 3.6V per cell. This gently charges the battery to 100% capacity before automatically cutting off.
Solar charging is also viable if using an appropriate PWM/MPPT solar charge controller preset to LFP charging voltages. Some lead-acid chargers may work too if their voltage limits aren’t too high.
Can lead-acid chargers charge lithium batteries?
While lead-acid chargers can potentially charge LFP batteries without damage, there are better alternatives. Most lead-acid chargers have higher voltage termination points unsuitable for LFP chemistry. This could cause overcharging and reduce battery life.
t’s safest to use an LFP-compatible charger with adjustable voltage set to the battery manufacturer’s recommended levels. Lead-acid chargers lacking adjustable voltages carry an overcharging risk and aren’t recommended.
Charging precautions
When charging LFP batteries, follow several precautions:
- Don’t exceed manufacturers’ recommended charge current (e.g. <=1C). High currents can cause overheating and degradation.
- Ensure charge voltage doesn’t exceed the max level (e.g. <=3.6V per cell). Overvoltage charging damages batteries.
- Don’t charge at temperatures below 0°C without reducing current. Cold temperatures impede chemical reactions.
- Ensure bank balancing for multiple parallel batteries. Uneven charge among batteries will cause capacity loss over time.
Long-term storage
For extended storage, keep LFP batteries between 40-60% state of charge to avoid excessive self-discharging. Their low self-discharge rate permits storage without maintenance charging for 6-12 months.
Recharge stored batteries to 90% every 6 months to maintain capacity. Fully recharge before returning to service. Avoid storing at 0% or 100% state of charge which can degrade battery health. Proper long-term storage protects your investment.
In conclusion, following charging best practices protects your LFP batteries and maximizes their performance for many years. Use an appropriate lithium-compatible charger, monitor charge voltages and temperatures, and store judiciously to keep batteries healthy.



